Reducing Electrical Noise in Vibration Testing Systems
Reduce unwanted electrical noise during vibration testing - Contact Sentek Dynamics for technical support or engineering services.
Sentek Dynamics vibration testing system featuring Crystal Instruments Spider-81 vibration controller and Engineering Data Management (EDM) Software.
Noise is an unwanted disturbance in electrical signals. It is an error or undesired random disturbance of a useful information signal. [1} Electrical noise can have adverse effects on testing.
Pre-test is a feature of Crystal Instruments’ Engineering Data Management (EDM) software. A lower level random test is conducted to ensure a closed control loop is established during testing and to estimate the Frequency Response Function (FRF) for random tests. Electrical noise can impact the FRF calculations, thereby affecting the control of the test.
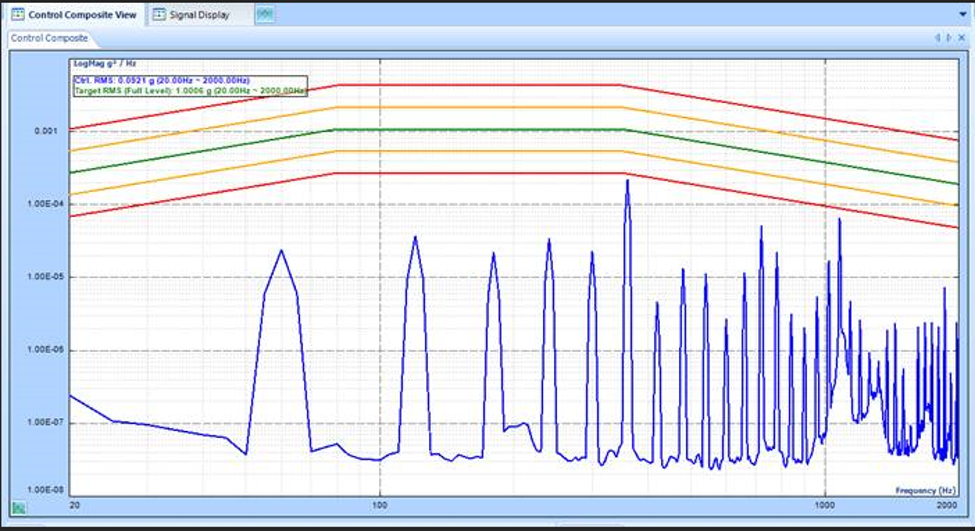
Users can check the noise floor of the system by loading the default Random profile and running the Check Only function in EDM. The payload, head expander, and slip table can act as an antenna and pick up ambient signals. Typically, the noise should be less than the order of magnitude of 1e-5 g2/Hz. Noise can be attributed to changes in cabling, the addition of equipment, sensor calibration, an unshielded Ethernet cable, and more.
Noise in a system can be reduced by:
Using a shielded Ethernet cable to connect the controller to the computer.
Using low noise coaxial sensor cables. [2]
Using a low noise BNC cable to connect the controller to the amplifier.
Using Kapton tape and gluing the accelerometer to the worktable and/or Device Under Test (DUT), which helps avoid the transmission of noise collected by the payload, head expander, and/or slip table.
References: